Web application firewalls are like personal security guards for your apps, giving you extra protection against cyber threats like cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks that regular defenses might miss.
What is a Web Application Firewall?
A web application firewall (WAF) protects web applications like a protective shield, filtering out harmful data and keeping your web applications safe.
How web application firewall architecture works?
WAF is super flexible, with customizable security policies that adjust to new threats, so your defenses stay ready no matter how the cyber landscape changes.
A WAF works at Layer 7, focusing on protecting specific applications instead of the whole network, unlike traditional firewalls that cover broader infrastructure.
Characteristics and Features
- Attack Detection and Prevention: WAFs work by using security rules and spotting unusual behavior to block attacks. They analyze traffic to stop threats before they even reach your web apps. Plus, they’re smart enough to catch new, unknown threats by recognizing malicious traffic patterns, like zero-day attacks.
- Granular Rule Configuration and Security Models: WAFs boost security by using customizable rules and blending two approaches: positive security (allowing safe behaviors) and negative security (blocking attack patterns). This combo helps keep things protected while staying accurate.
- Bot Detection and Mitigation: WAFs use tools like CAPTCHA and rate limiting to stop malicious bots in their tracks, keeping your site safe from attacks, data scraping, and other automated threats
- Session and Data Protection: WAFs help keep user sessions safe by stopping hijacking and similar attacks. They also protect sensitive data by keeping an eye on outgoing responses to prevent any breaches.
- Content Inspection and Filtering: WAFs help keep your data safe by filtering out and blocking harmful content.
- Security Logging, Reporting, and Real-time Monitoring: WAFs help you catch threats in real time and respond quickly, all while keeping detailed logs for audits, web application security compliance, and post-incident reviews.
- Integration with Threat Intelligence and Virtual Patching: WAFs use threat intelligence to stop new threats, malware, and malicious IPs in their tracks. They also work like virtual patches, blocking known vulnerabilities until they can be properly fixed.
- SSL/TLS Offloading and Inspection: WAFs work by decrypting, checking, and re-encrypting SSL/TLS traffic to catch any malicious content before it reaches your web applications.
WAF vs Firewall
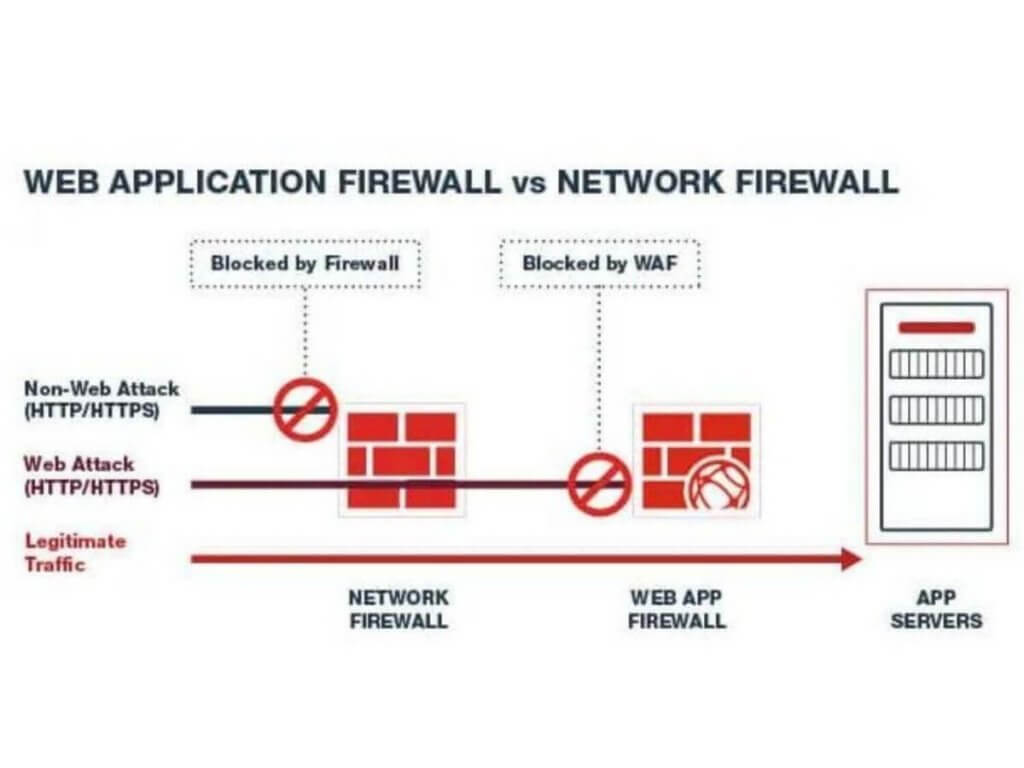
Network firewalls come with useful features like VPN compatibility, packet filtering, deep packet inspection, antivirus, and website blocking.
Next-generation firewalls take it a step further by including intrusion detection systems and intrusion prevention systems, but they can still have a hard time dealing with application vulnerabilities.
That’s where Web Application Firewalls come in. WAFs are great for defending against application-layer attacks.
They can adapt in real time, block potential threats, and even help prevent DDoS attacks on multiple levels.
Why is it Important?
Data breaches aren’t just frustrating—they’re costly too. According to the Data Breach Report, the global average cost of a data breach in 2024 has hit an all-time high, up 10% from last year.
Web Application Firewalls are a must-have when it comes to keeping your website safe from threats. These attacks can put your data at risk, slow things down, or even take your site offline.
But WAFs don’t just protect you—they also help you stay compliant with regulations like PCI DSS and GDPR, so you can avoid fines and protect your reputation.
Types of Attacks a WAF Can Prevent
Attackers can inject malicious code by exploiting untrusted data sent to an interpreter as part of a command or query.
Injection
Attackers can inject malicious code by exploiting untrusted data sent to an interpreter as part of a command or query.
Broken Authentication
Hackers can assume other users’ identities through compromised passwords, API tokens, or other authentication flaws.
Sensitive Data Exposure
Cybercriminals may steal or modify weakly protected sensitive data to commit credit card fraud, identity theft, or other crimes.
XML External Entities (XXE)
Poorly configured XML processors evaluate external entities which can be used to exploit and disclose internal files.
Broken Access Controls
Improper restrictions on authenticated users are to be exploited by attackers to access confidential files without authorization.
Security Misconfiguration
Insecure or incomplete default configurations can lead to security misconfiguration, which contributes to a breach in a web application.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
XSS vulnerabilities in a web application often lead to script execution without validation by hackers who can hijack user sessions.
Insecure Deserialization
Insecure deserialization enables cybercriminals to perform an attack on a web application by executing code and gaining remote access to web databases.
Known Vulnerabilities Components
Components with known vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers because it runs with the same privileges as the application.
Insufficient Logging and Monitoring
Insufficient logging and monitoring without effective incident response enable hackers to further attack and maintain persistence.
Bad Bots
Bad bots often mimic human interaction to perform attacks such as web scraping, data mining, account takeover, and transaction fraud.
Malicious Uploads
Web applications that enable users to upload their own content are vulnerable to malicious code payloads from cybercriminals.
Unknown Vulnerabilities
Attackers are increasingly adept at disguising their code to exploit web application security flaws with no signatures that exist before on a web application.
Zero-Day Attacks
Any newly discovered vulnerabilities on a web application are to be misused by hackers to perform a cyberattack on the same day.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
Cybercriminals may attempt to overwhelm a web application with unusual levels of malicious web traffic from different sources at the same time.
Read more: Cyber Security Threat.
Setting up a Web Application Firewall
Web application firewalls (WAFs) all have their pros and cons, so it’s important to know what sets them apart to pick the right one for you.
Physical Hardware

A hardware-based WAF is basically a physical device that sits near your web servers, filtering data packets right at the source.
It’s superfast and great for handling high traffic, making it perfect for big companies that need top performance.
The downside? It’s expensive to buy, set up, and maintain, so it’s not the best option for smaller organizations.
VM or Virtual Machine
A software-based WAF runs on a virtual machine or server plugin instead of physical hardware, giving you the flexibility to use it on-premises or in the cloud.
It’s a more budget-friendly option compared to hardware WAFs, but it can be a bit slower due to higher latency.
It’s a popular choice for large enterprises with cloud servers and smaller businesses looking for affordable web application protection.
Cloud via SaaS
A cloud-based WAF is a plug-and-play solution—no need to install or worry about maintenance. It’s super easy to use, with a subscription model and automatic updates handled for you.
While it’s not the most customizable option, it’s perfect for small to medium-sized businesses that don’t have the time or resources to manage a WAF themselves.
Best WAF Solution: Fortinet FortiWeb
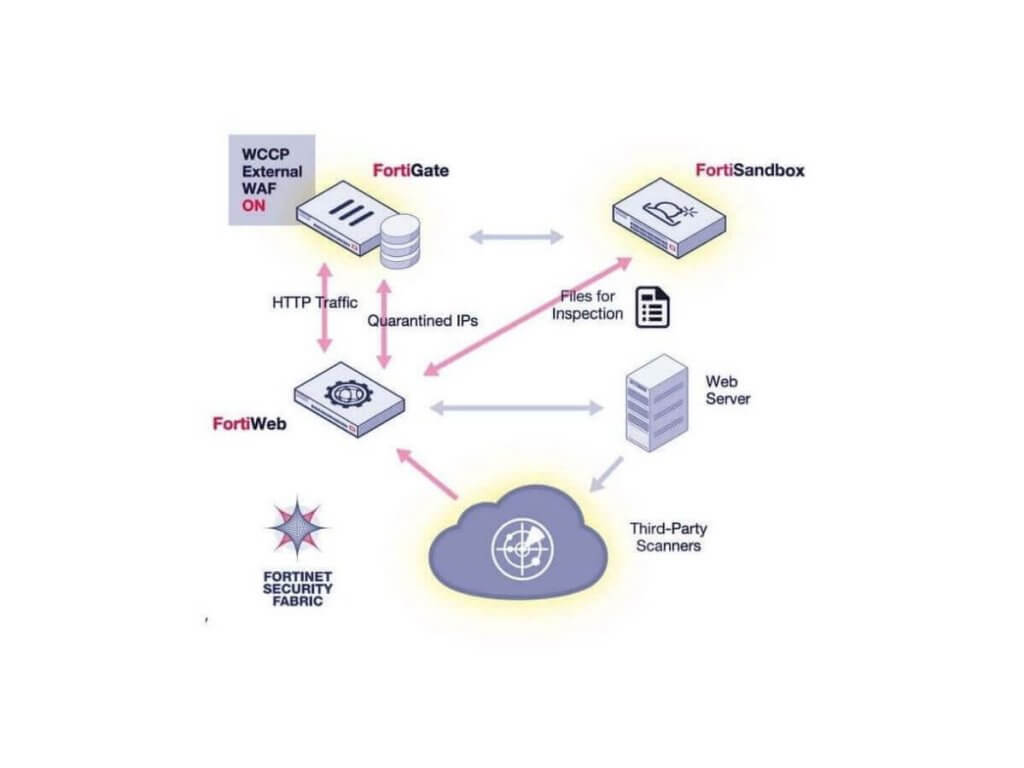
FortiWeb is your go-to web application firewall, designed to protect your critical web apps from both known and unknown vulnerabilities.
It’s easy to set up and manage, offering strong security whether you’re using virtual, hybrid, or hardware environments.
Plus, it works seamlessly with top hypervisors like VMware and Hyper-V, as well as cloud platforms like AWS and Azure.
WAF vs NGFW
Next-generation firewalls include a solid traditional firewall base, including VPN compatibility and basic packet filtering, as well as deep packet inspection, antivirus inspection, website blocking, and a slew of additional network security features.
In reality, intrusion prevention systems, or IPS, are included in many next-generation firewalls. Although NGFWs provide additional protection, they are typically incapable of dealing with application vulnerabilities.
A Web Application Firewall, on the other hand, is typically a cloud-based appliance with sophisticated rules to protect against common application-layer attacks such as SQL Injection, Cross-Site Scripting, and Cross-Site Request Forgery.
Above all, WAF may be set up to learn new rules in real-time and block possible attacks. It also aids in the prevention of DDoS attacks on multiple levels.
Web Apps Protection in Malaysia

Keep your business safe with Spectrum Edge, Fortinet distributor in Malaysia. We’ve got the best cybersecurity solutions you need to protect your web apps and keep online threats at bay.
You focus on growing your business—we’ll handle the digital security. Ready for hassle-free protection? Contact us today!


